There are many children’s footwear categories, such as leather shoes, dress shoes, canvas shoes, casual shoes, sports shoes, hiking shoes, winter boots, sandals, moccasins, etc.
The process varies due to different shoe styles and constructions in common sense.
From the initial design and development, where prototypes of the shoes are created, to the final assembly and finishing touches, each step in the process is carefully executed to ensure that the finished product is of the highest quality and comfortable for children to wear.

In this blog post, we will take a closer look at how kids’ shoes are made in the shoe factory, from design to production.
I. Design and Development
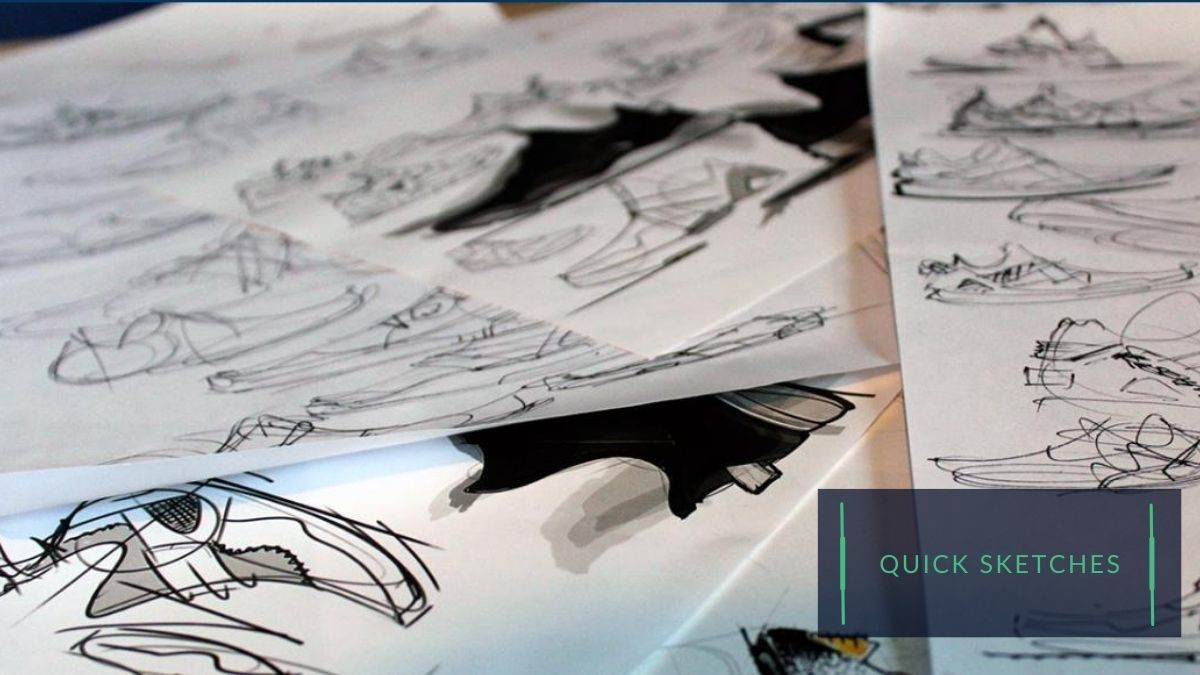

I.I The importance of comfort and fit in kids’ shoe design
Children’s feet are still developing, and their shoes must provide support and comfort to allow them to move and play comfortably.
Poorly fitting or uncomfortable shoes can cause problems such as blisters, foot pain, and even long-term foot deformities.
When designing kids’ shoes, designers must consider the specific needs and characteristics of a child’s foot and healthy foot development.
This may involve using specialized materials and features, such as padded insoles and flexible soles, to ensure that the shoes are comfortable and supportive.
In addition to comfort, the proper last is also crucial. Kids’ shoes must fit properly to support their feet and allow them to move and play comfortably.
I.II How to design and develop kids’ shoes?
The design and development of kids’ shoes involve several steps and considerations. Some of the key steps in the process include:
Research:
Before starting the design process, designers will typically conduct research to understand the needs and preferences of the target market for the shoes. This may involve researching trends and customer feedback, as well as analyzing data on child`s foot size and shape for children in different age groups.
Sketching and prototyping:
Once the research phase is complete, designers will begin sketching out ideas and concepts for the shoe. These sketches may be refined and modified using computer-aided design (CAD) software. After that, the CAD will be passed to the development center to realize the prototype sample.
Fitting Test and refining:
After the initial prototypes have been created, they are subjected to wearing tests and refinement. This may involve getting feedback from kids, wearing the shoes for extended periods to test for comfort and durability, and making any necessary modifications to the design.
Especially the feedback of the last and the outsole is crucial.
Finalizing the samples:
Once the creation of the shoes has been completed, the confirmation samples and sales samples for promotion will be requested.
This process will include details such as the accurate materials to be used, the specific dimensions of the logo, and any special features or details to be included.
Overall, the design and development of kids’ shoes is a multifaceted process that requires creativity, technical expertise, and attention to detail.
By considering the needs and preferences of the target market and subjecting the prototypes to rigorous testing and refinement, designers can create shoes that are both stylish and comfortable for children.
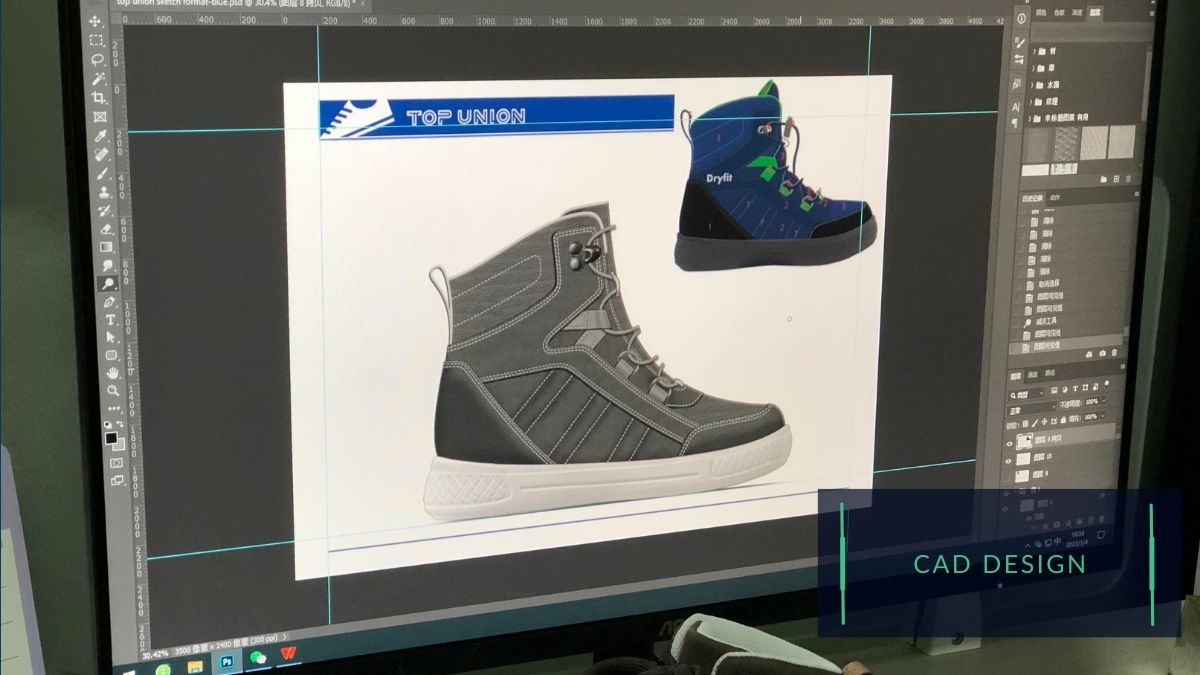

II. Material Selection
II.I The types of materials used in kids’ shoes
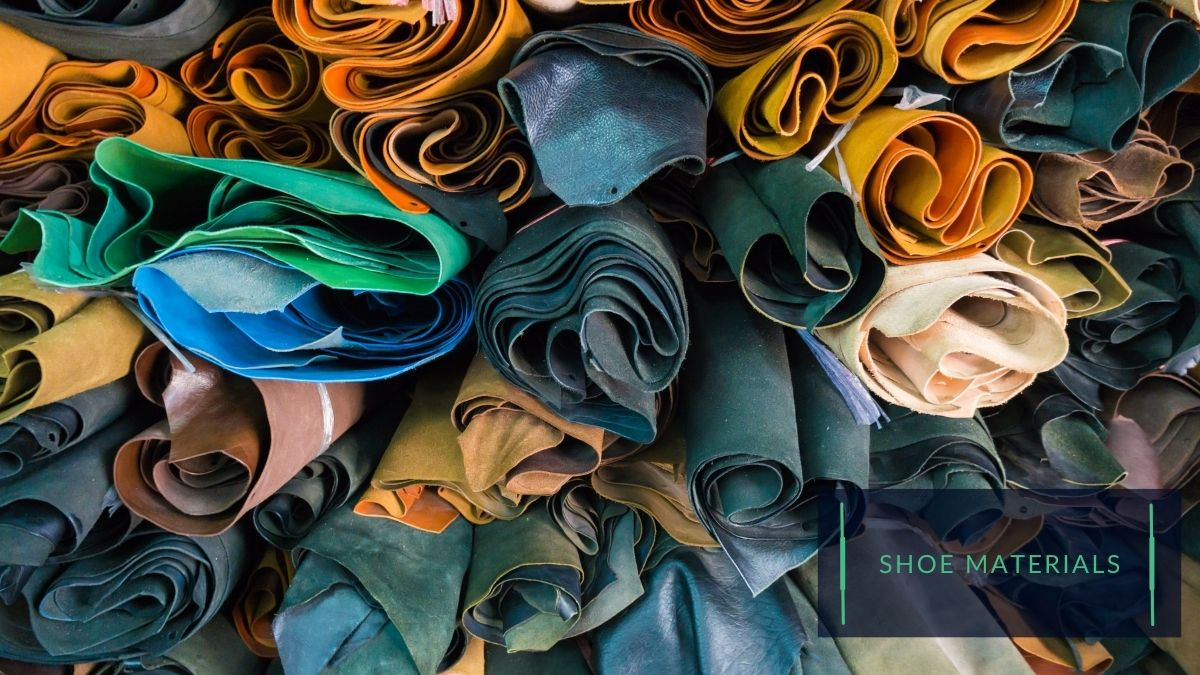

Several types of materials can be used in the production of kids’ shoes, including materials for the uppers, lining, outsole, insock, and other components.
1) Materials for uppers:
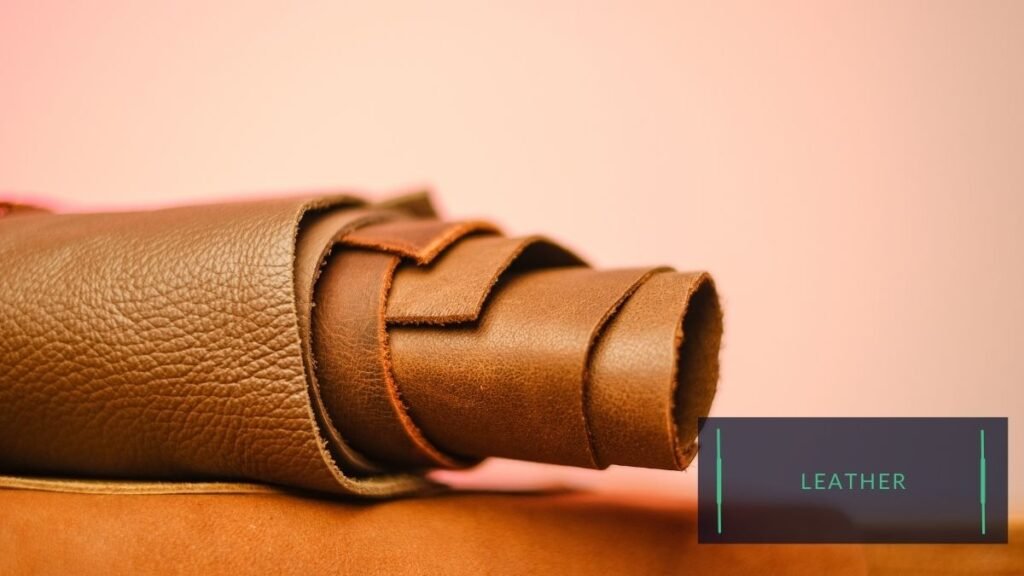

Leather:
Leather is a popular choice for the uppers of kids’ shoes, as it is durable and breathable. It can be treated to be water-resistant or waterproof.
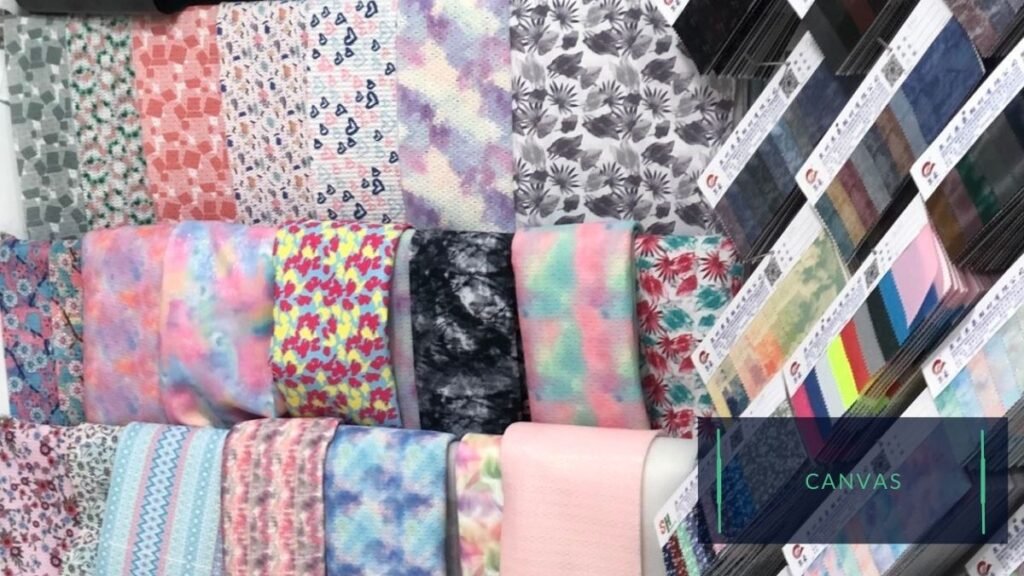

Canvas:
Canvas is another common material used for the uppers of children’s shoes. It is lightweight and breathable, making it a good choice for casual shoes or sneakers. Canvas can also be printed on, allowing for a wide range of design options.
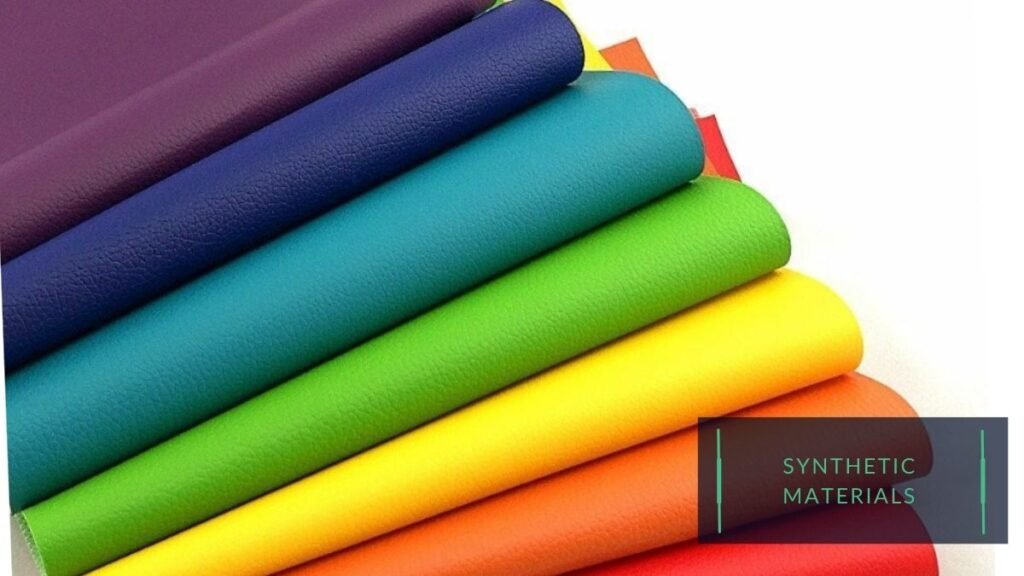

Synthetic:
Synthetic materials such as polyester, nylon, and polyurethane are generally less expensive than leather.
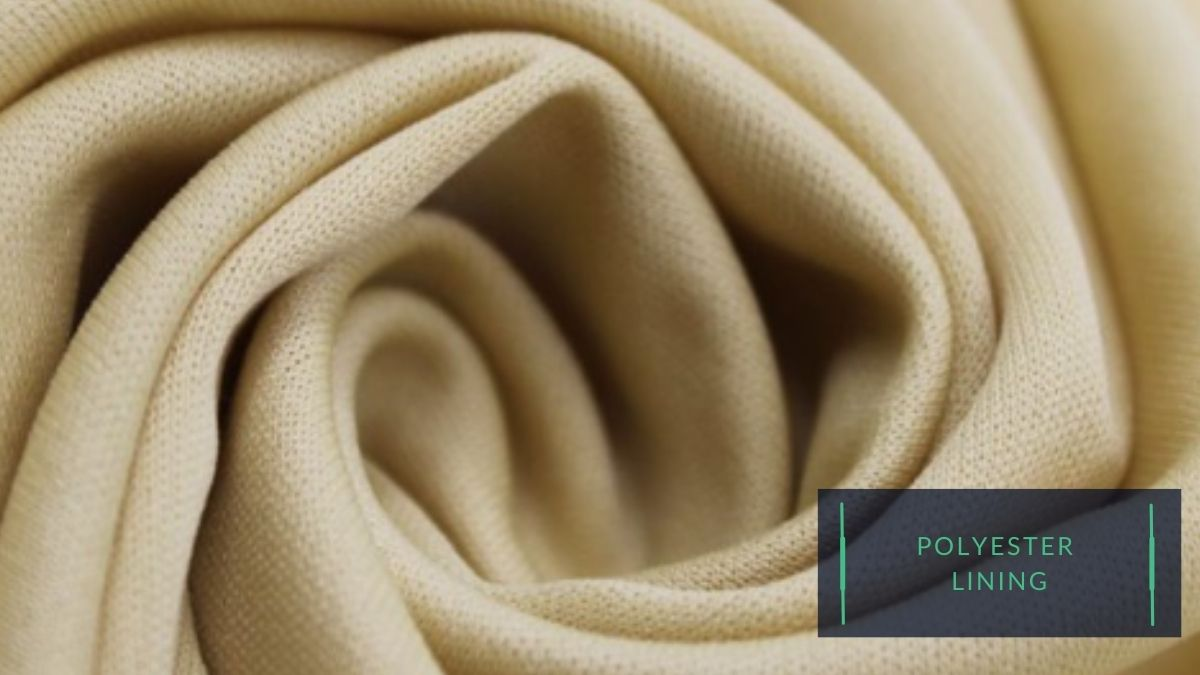
2) Lining materials:
- Leather: Sheepskin leather and pig skin leather are often used as a lining material for kids’ shoes, as it is soft and comfortable against the skin. It is also breathable and durable, making it a good choice for shoes that will be worn frequently.
- Textile materials, such as cotton, wool, and polyester, are also used for the lining. These materials can be treated to be moisture-wicking or antimicrobial, and they can help to keep the child`s foot cool and dry.

3) Outsole materials:

Rubber is a popular choice for the outsole, as it is durable, slip-resistant, and can withstand wear and tear. Rubber outsoles are also generally flexible, which is vital for the natural movement of the feet.
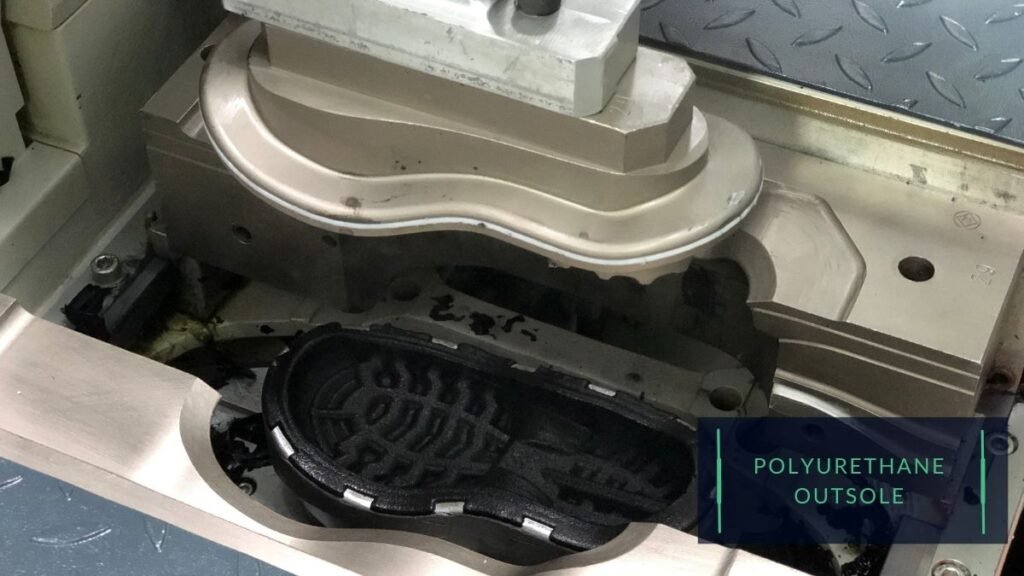

Polyurethane (PU) and thermoplastic rubber (TPR) are also used for the outsole of child shoes. These materials are generally less expensive than rubber and can be molded into various shapes and patterns.
4) Insock Materials:
- Foam materials such as memory foam and EVA foam are commonly used for the insock of kid shoes. These materials are soft and comfortable against the skin, and they can help to absorb shock and cushion the feet.
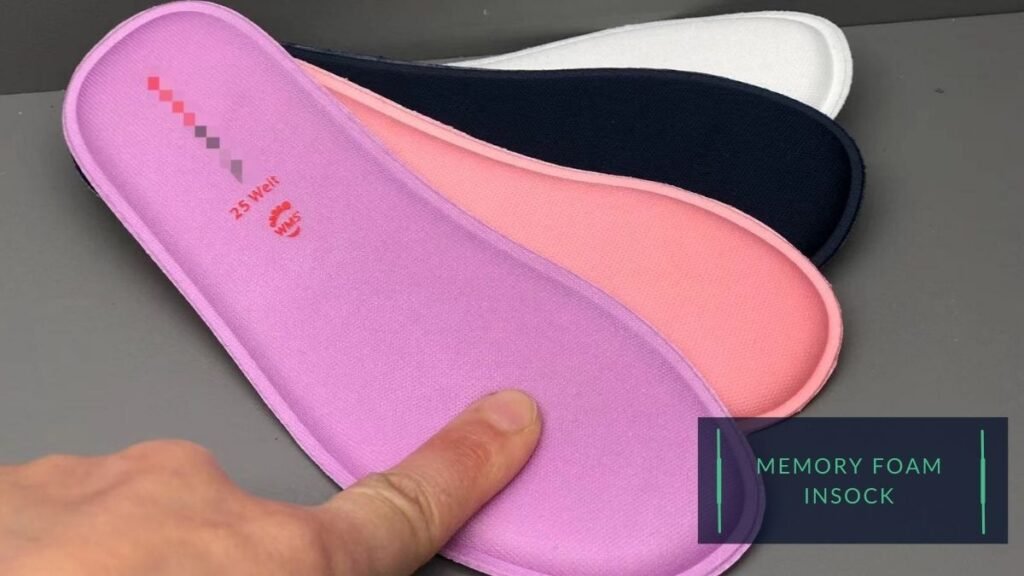

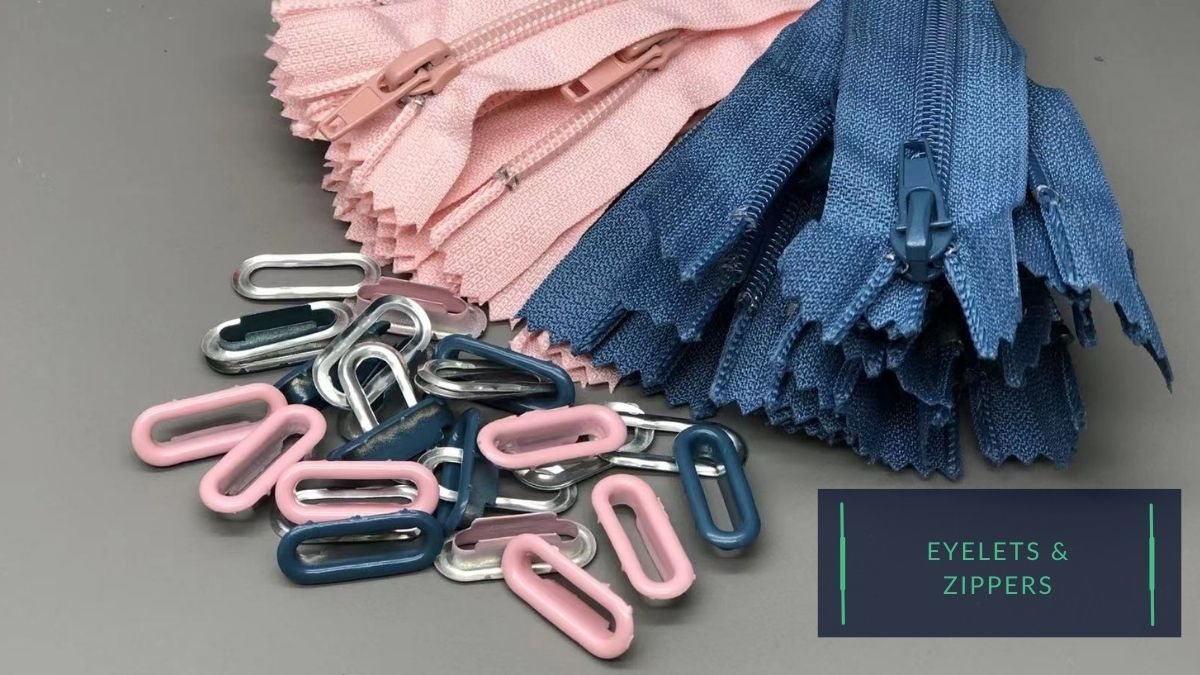
5) Other materials:
- Various other materials may be applied to manufacture children’s shoes, such as metal eyelets, and plastic lace locks. These materials are chosen based on their specific properties and the needs of the different shoe styles.

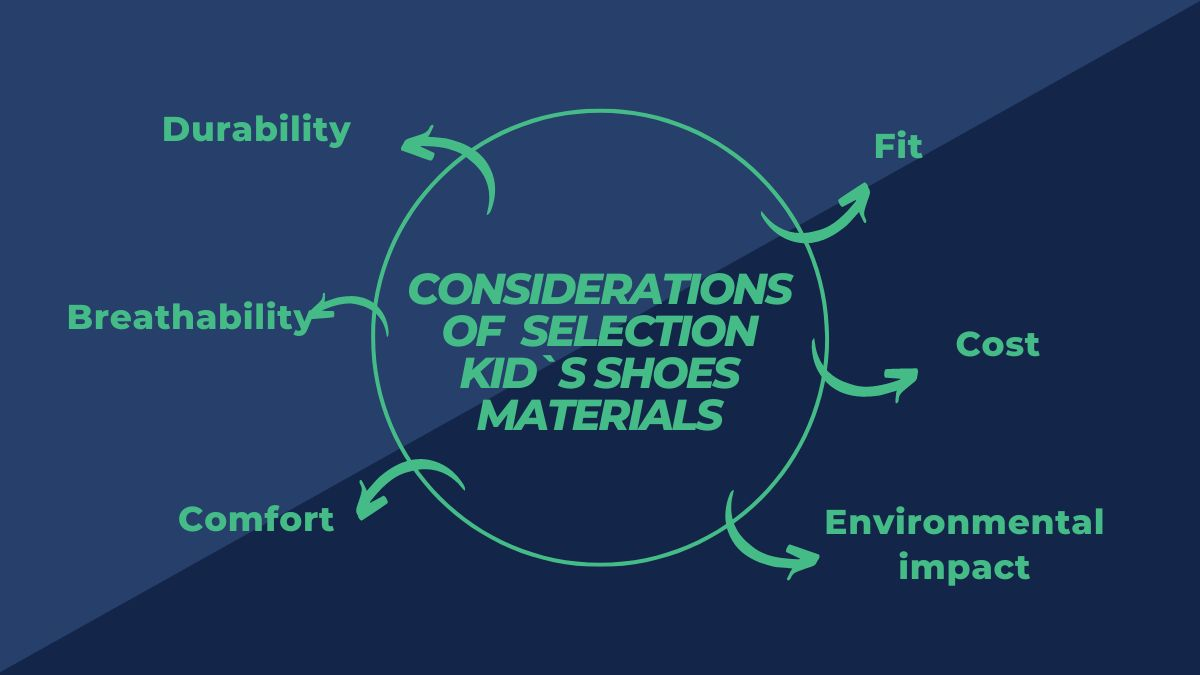
II.II The considerations for selecting materials

Several considerations go into the selection of materials for the manufacturing of kids’ shoes. These may include:
- Durability:
The materials used in kids’ shoes need to withstand the wear and tear of everyday use, as well as the rough and tumble nature of children’s play. Materials that are durable and able to withstand abrasion and impact are generally preferred. - Breathability:
Children’s feet tend to sweat more than adult feet, so it is crucial to choose materials that are breathable and allow for airflow. Non-breathable materials can lead to foot odor and discomfort. - Comfort:
The materials should be comfortable against the skin and provide cushioning and support for the child`s foot. Soft, flexible materials that conform to the foot’s shape are generally preferred. - Fit:
The materials should provide a good fit and support the natural shape of the feet. Materials that are too stiff or inflexible can cause discomfort and difficulty walking. - Cost:
The cost of the materials is also a consideration, as it will impact the overall price of the finished product. Manufacturers may need to balance the cost of the materials with the other desired properties. - Environmental impact:
Some manufacturers may also consider the environmental impact of the materials used in kid shoes, choosing sustainable or recycled materials.
By carefully considering these factors, manufacturers can choose suitable materials to create high-quality, comfortable, and well-fitting kids’ shoes.
III. Material Cutting

III.I The process of cutting out the various shoe parts from the materials
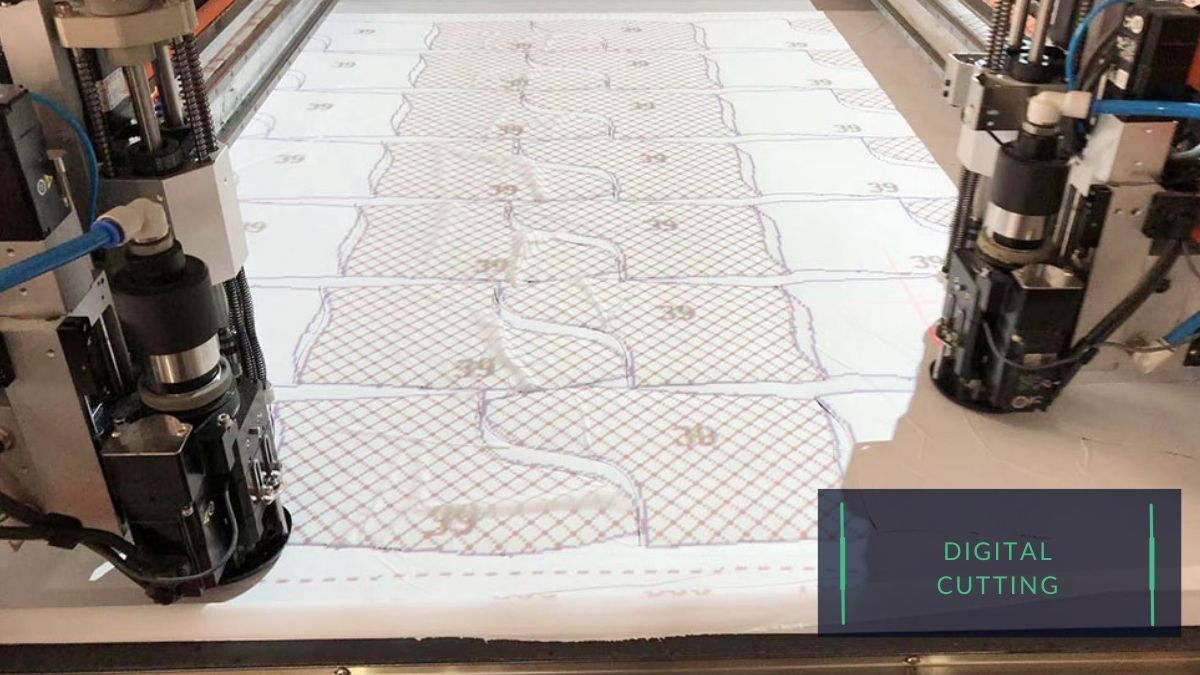
Digital cutting and manual cutting are methods that can be used to cut out shoe components.
Digital cutting involves the use of specialized machines that are equipped with cutting blades or lasers. These machines are programmed with the precise dimensions and shapes of the various parts of the shoe, and they can cut out the parts with high accuracy and efficiency.
Digital cutting is generally faster and more precise than manual cutting, and it is well-suited for large-scale production runs where a high level of consistency is required.

Manual cutting involves using hand-held cutting tools such as cutting dies (the knife mold as the shoe components) to cut out the various parts of the shoe. This method may be used for more rigid materials that cannot be easily cut using a machine.
Manual cutting requires a high skill level and experienced workers, as the cutting tools must be accurately positioned and applied to achieve the desired shapes and dimensions.
And it is not as effective as digital cutting in speed and efficiency. However, manual cutting can be more cost-effective for small-scale production runs, as it does not require expensive cutting machines.
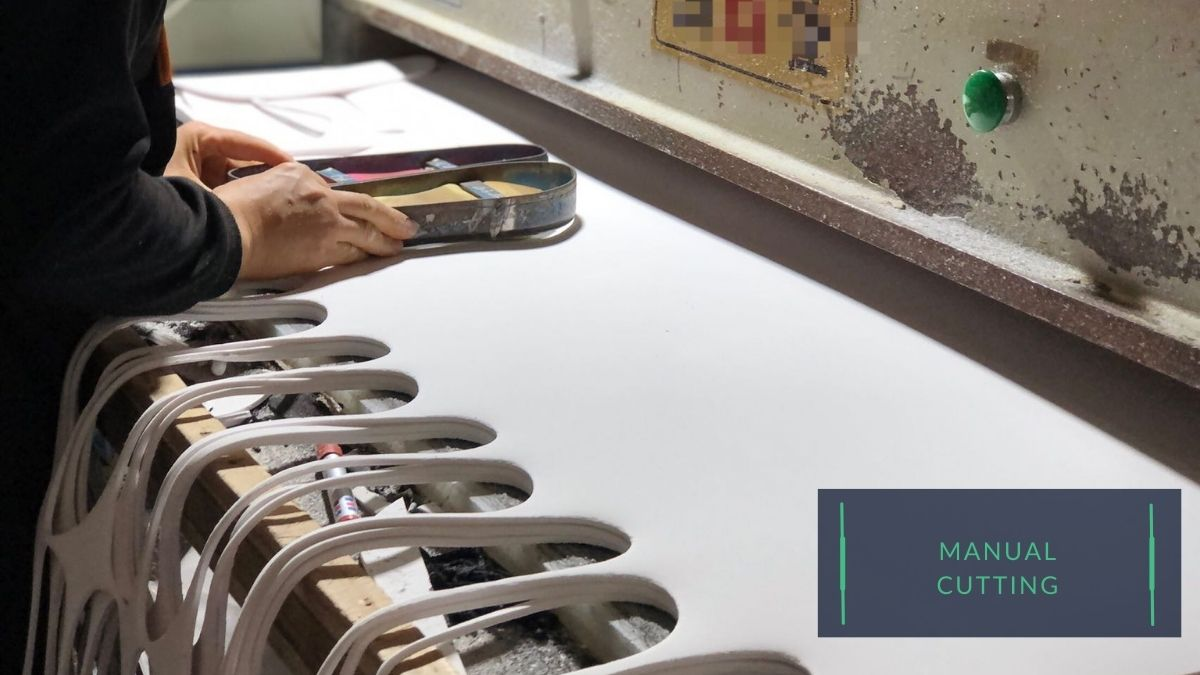

Overall, the choice between digital cutting and manual cutting will depend on the specific materials and design of the shoes, as well as the size and scale of the production run. The factory must consider these factors when deciding which method is the most appropriate for its needs.
IV. Material Components Sewing

IV.I The sewing process
In recent years, computerized stitching has become increasingly common in the shoe manufacturing industry, offering several advantages over traditional methods.
By using computer-controlled needles and threads, the factory can produce footwear that is more uniform in terms of stitching quality and appearance. This can be especially important for large-scale production runs, where a high level of consistency is required.
In addition to the benefits of consistency, computerized stitching also offers advantages in terms of speed and efficiency. These machines can sew the parts of the shoe together much faster than traditional hand-sewing methods, which can reduce production times and costs.
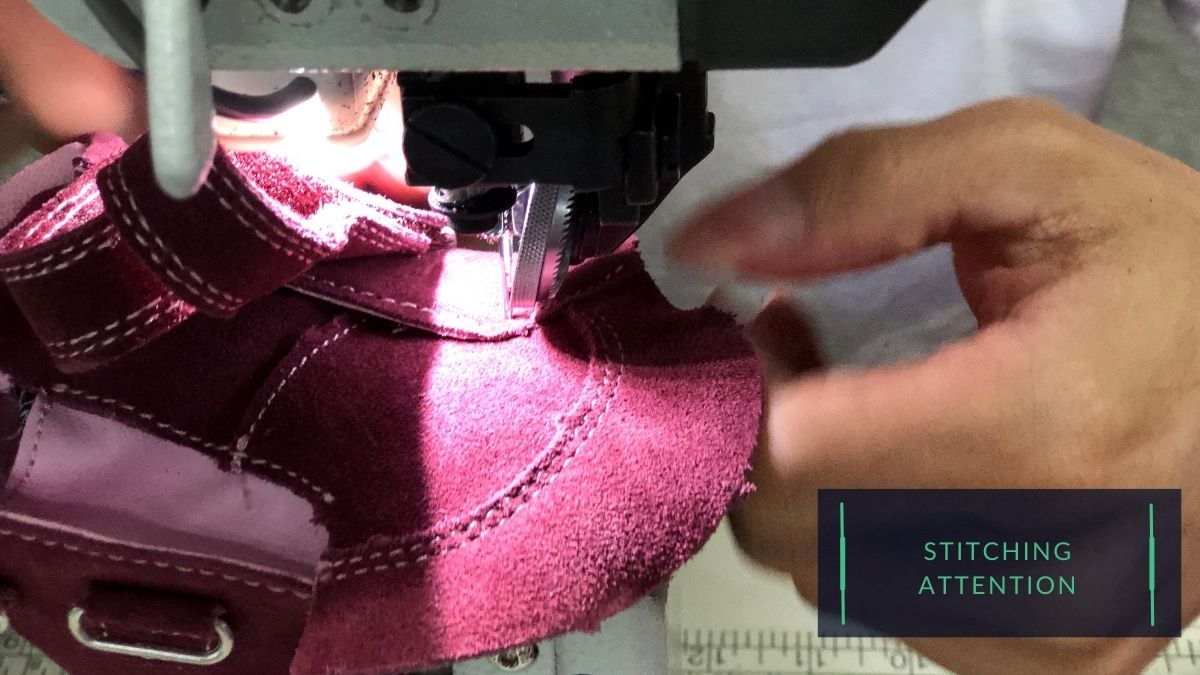
IV.II The attention to sewing kids’ shoes
Some of the key considerations for sewing kids’ shoes include the following:

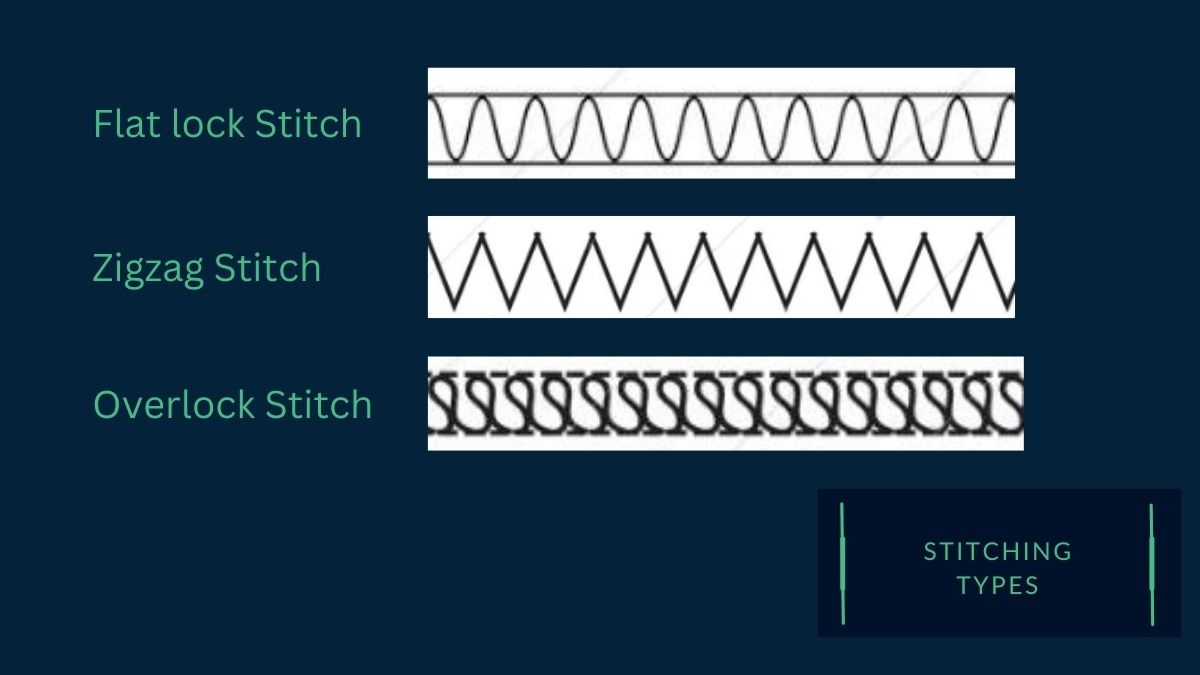
Stitching types:
The type of stitching used for sewing children’s shoes should be strong and durable, able to withstand the wear and tear of everyday use. Stitch types such as the lockstitch, zigzag stitch, and overlock stitch are commonly used in the production of kids’ shoes, as they offer a robust and secure seam that can withstand abrasion and tension.
Stitching tension:
The tension of the stitch used for sewing kids’ shoes should be carefully balanced to achieve a robust and secure seam. Stitches that are too loose may be prone to unraveling, while stitches that are too tight may cause the material to pucker or distort.
The attention to detail and care that goes into the sewing of children’s shoes is critical to the quality and comfort of the finished.
V. Assembling and Finishing

Assembling children’s shoes involves bringing the stitched upper and sole together to create the finished product. Several methods can be used for this process, including cementing, vulcanization, direct injection, Goodyear welting, and others.
Cementing:
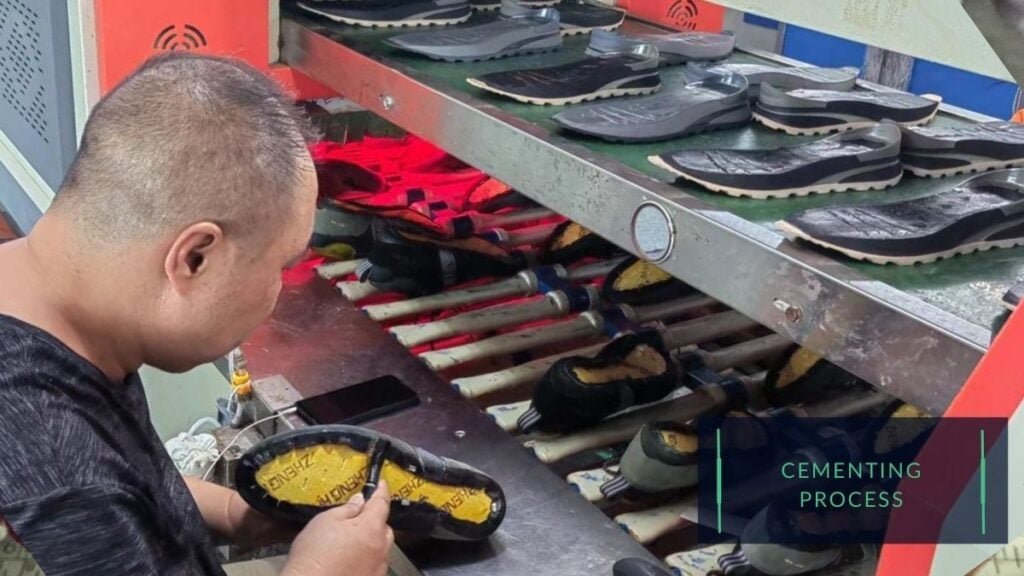

Cementing is a common construction method, and it involves using adhesives to bond the upper and outsole of the shoe together.
The advantage of cementing is that it is a relatively simple and cost-effective method. Still, it may result in a less durable and flexible shoe than other construction methods.
Vulcanization:
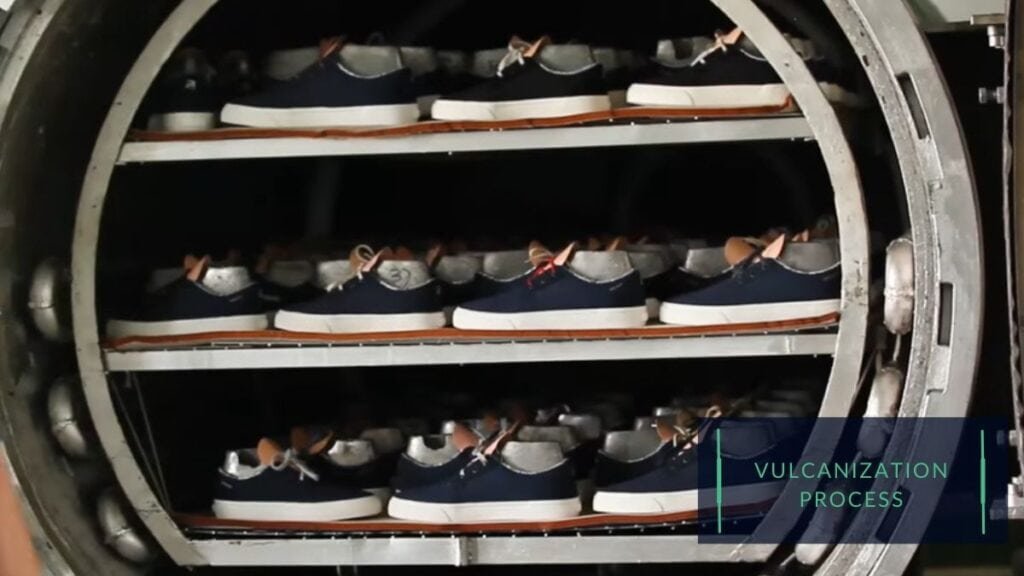

Vulcanization: the sole is attached to the upper using a specialized rubber compound that is heated and cured to form a strong bond.
Vulcanization allows for creating a strong, durable, and flexible shoe, but it can be more time-consuming and expensive than other construction methods.
Direct injection:
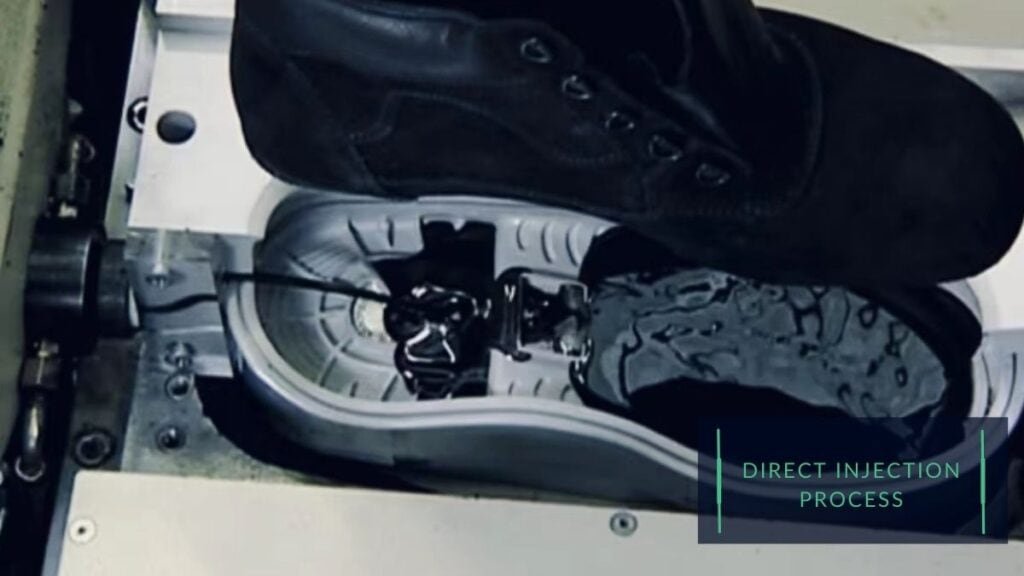

Direct injection, also known as DIP, is a technique used to inject the liquid sole material (usually a polymer) directly onto the upper and quickly mold. This results in a seamless bond that creates a solid and durable shoe.

The direct injection molding process begins with the finished shoe upper (hold with the lasted) being placed over a sole-shaped mold at the injection molding machine.
The liquid material is then heated and injected into the aluminum sole mold cavity instantly around the upper, with a high mixing speed of over 18000 RPM, creating a better grain structure. It rapidly molded to the upper directly, resulting in a permanent bond.
Goodyear welting:
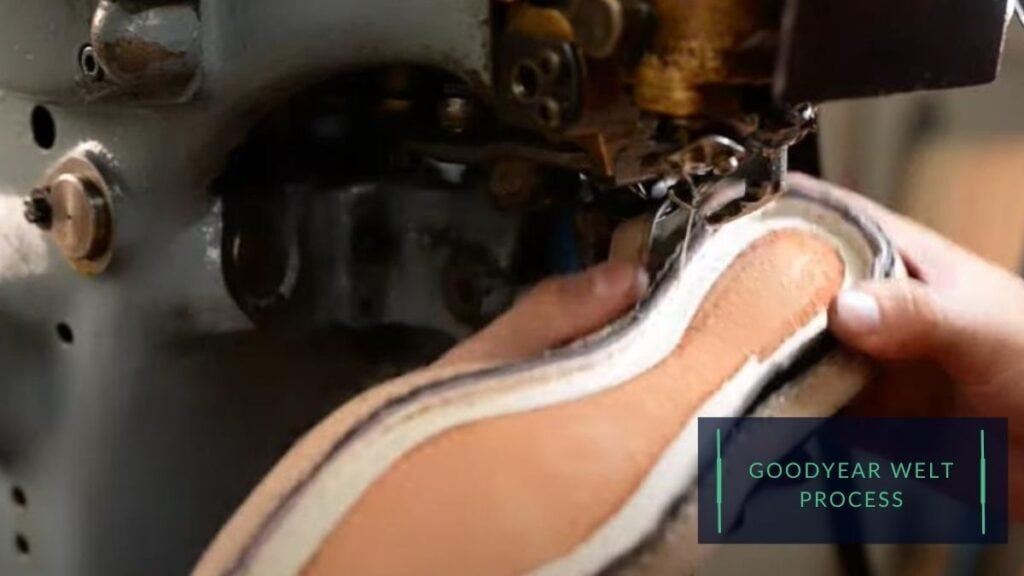

Goodyear welting is a construction method that involves using a strip of leather or other material to create a strong, durable seam between the outsole and upper of the shoe.
This method allows for creating a high-quality, long-lasting shoe, but it can be more time-consuming and expensive than other construction methods.
Overall, assembling kids’ shoes will depend on the specific construction method used, and manufacturers will need to choose the most appropriate method based on the desired properties and cost of the finished product.
VI. Quality Check and Inspection

The final quality check and inspection process is an essential step in producing kids’ shoes, as it ensures that the finished product meets the required standards of quality and safety. This process typically involves a thorough examination of the shoes by a team of trained quality control personnel, who check for defects, flaws, or other issues that may affect the performance or durability of the shoes.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of making kids’ shoes is a complex and intricate process that involves a wide range of skills and techniques. By carefully following each step and using high-quality materials, manufacturers can create shoes that are suitable for a variety of activities, and that meet the needs of children of different ages.
“Just Click Here to get Free Samples & Quick Quote for your Order.”
If you are a brand owner or a wholesaler looking to buy unique & customs designs kids’ shoes, then we, Dryfitmax®, can be a one-stop solution for you. In our 20,200 square meters factory, 100+ skilled persons produce more than 2000+ pairs of shoes daily. So, you can expect the quickest deliveries even in peak seasons.

















